Does your knee feel stiff when you wake up? And not just for a short time, but the soreness persists throughout the day and becomes better as you walk? Does that sound familiar? You’re not alone. It could be one of the most prevalent joint issues, particularly as we age or put greater strain on our joints. Knee Osteoarthritis (OA). Wondering what osteoarthritis in the knee exactly is? Read through!
Knee Osteoarthritis: What Is It?

Knee Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, is one of the most commonly occurring joint issues, especially if you are aging or put extra strain on your knees. This degenerative joint disease causes the cartilage that cushions your knee to progressively deteriorate. Your bones begin to scrape against one another directly when this cushioning disappears. This friction results in stiffness, discomfort, and edema.
Although it’s a chronic condition, which means it doesn’t go away entirely, many individuals can still enjoy active, satisfying lives if they receive the proper care and make correct lifestyle changes. Consider cartilage to be a kind of shock absorber. That absorber begins to degrade with age, trauma, or prolonged stress. This causes friction in the joint that starts to pain and make it rough to walk or do usual chores.
Knee Osteoarthritis Stages: What Takes Place Over Time
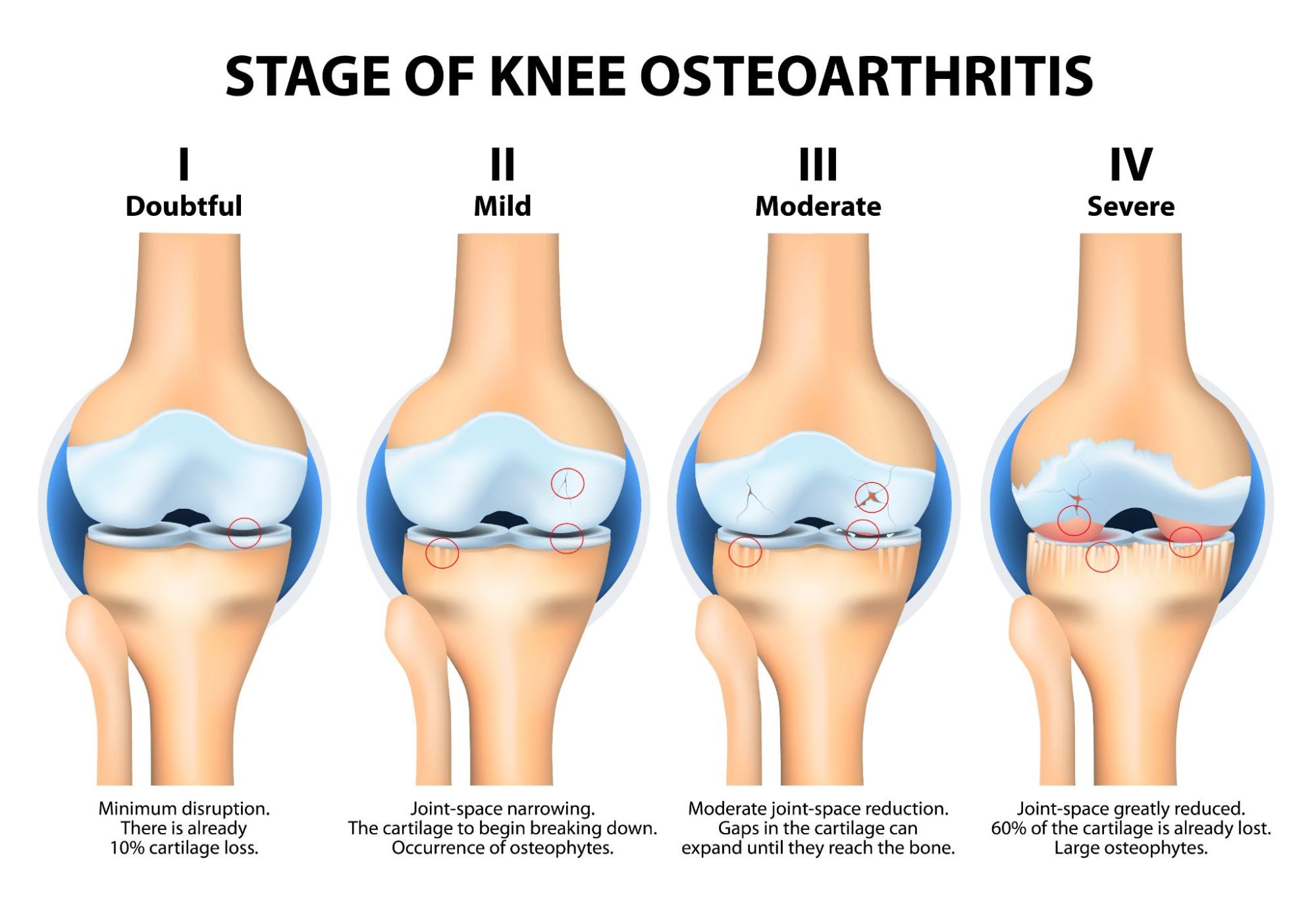
Knee Osteoarthritis doesn’t occur overnight or in a few days. It takes time to develop. It develops gradually and frequently in predictable stages. Being aware of your current situation will help you better control your symptoms and consult an expert. At Jain Multispeciality Hospital, all you need to do is look for the right doctor, and we will handle the rest of your journey. Here are the stages of Knee Osteoarthritis that you should know to recognize the early signs and symptoms.
Stage 1: Minor Modifications, No Pain As of Yet
At this point, you most likely won’t have any symptoms. There may be a minor thinning of the cartilage and the formation of tiny bone spurs. The majority of people aren’t even aware that anything is amiss yet.
Stage 2: The Start of Mild OA
You may now occasionally experience stiffness, particularly in the morning or after prolonged sitting. Although the distance between bones gets smaller, there is still enough cartilage to keep bones from touching.
Stage 3: Moderate OA, Initiation of Pain
The discomfort intensifies and lasts longer, particularly when walking, climbing stairs, or squatting. The level of inflammation rises. The loss of cartilage gets worse, and swelling and decreased flexibility may appear.
Stage 4: Severe OA
The cushioning cartilage is almost completely gone by this point. Direct bone-to-bone contact results in severe discomfort, stiffness, and edema. Your knee can freeze up or feel unsteady. Daily activities like bending or walking can become difficult. Many patients think about having a total knee replacement at this point.
Causes of knee Osteoarthritis
The most common and frequent cause? Time. Years of wear and tear are frequently the cause of OA. However, aging isn’t the only condition that might accelerate cartilage degradation. There are multiple reasons that slowly and gradually contribute to knee osteoarthritis.
Some of the primary causes and risk factors are as follows: