Millions of women suffer from polycystic ovarian syndrome, or PCOS, but only a few understand what it actually is. Knowing what PCOS is and isn’t can help you manage it properly, whether you’re dealing with symptoms yourself or are attempting to help someone who is.
Let’s discuss this hormonal disorder in more detail, covering what causes PCOS, symptoms, diagnosis, and the best treatment for PCOS. Keep reading for a clear picture of the disorder. Also watch this video for more insights about PCOS & PCOD.
What is PCOS?
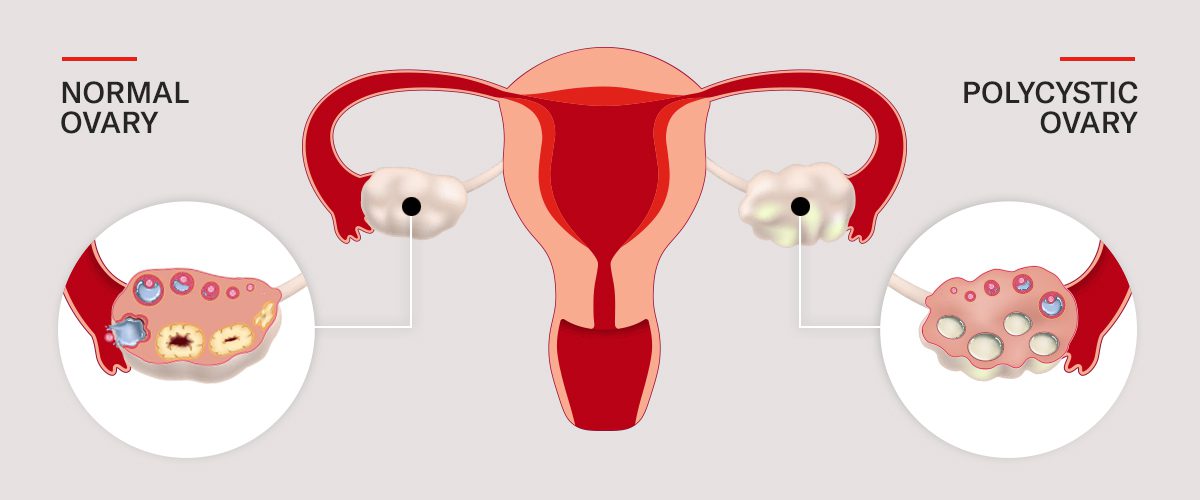
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, or PCOS, is a hormonal condition that mainly affects women who are in or nearing their reproductive age. It’s not just about ovarian cysts, despite the name. Reproductive hormone abnormalities, particularly the increased levels of insulin and androgens (male hormones), are a hallmark of PCOS. The development and release of eggs during ovulation may be hampered by these imbalances.
It’s estimated that between 6 and 13% of women in their reproductive years have PCOS, but even more shocking is the fact that up to 70% of them go untreated. And why do you think this happens? Mostly because of a lack of awareness. Most women take missing periods and other symptoms as normal when they are not. This is also partially due to the fact that symptoms can differ greatly and that many women are unaware that the changes in their bodies are caused by a hormone disorder.
When Does PCOS Usually Start?
Although PCOS symptoms might take years to identify or diagnose, they frequently begin in youth. In their 20’s or 30’s, most people learn they have PCOS, especially if they have problems getting pregnant. However, PCOS can appear differently in each individual and can occur at any point after puberty.
Symptoms of PCOS Problem in Females
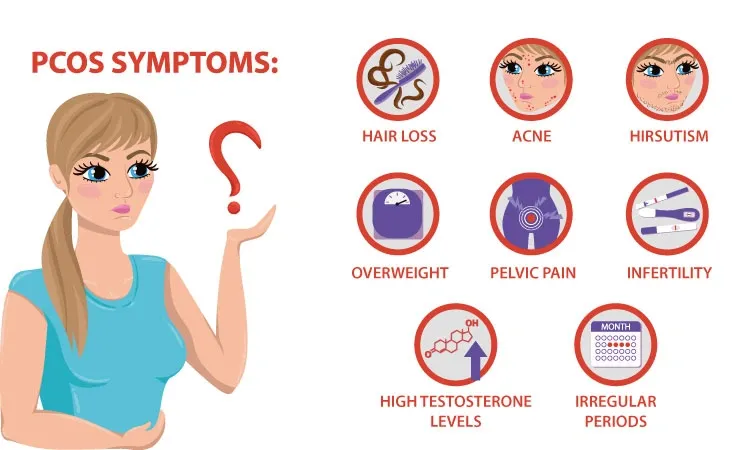
The symptoms of PCOS might vary greatly from person to person. While some women cope with multiple symptoms, others only have one or two. Age, weight, stress levels, and lifestyle choices can all have an impact on how severe these symptoms become over time.
Let us explore the most common PCOS symptoms that women usually experience if they have the disorder.